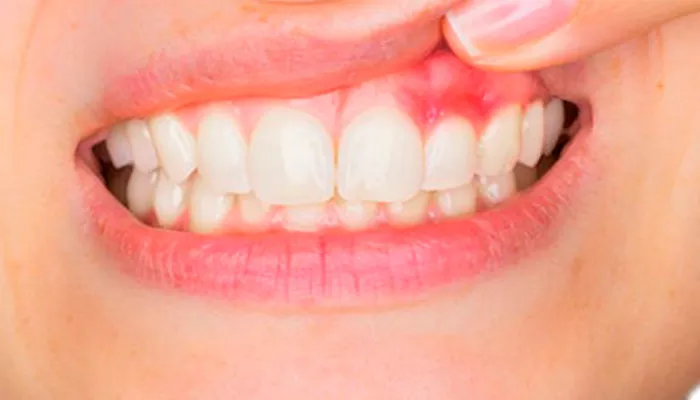
Gum infections, also known as periodontal infections, can lead to severe dental problems if not managed properly. A gum infection occurs when bacteria accumulate in the mouth, causing inflammation, swelling, and pain. While professional treatment is crucial, patient behavior significantly influences recovery. Knowing what not to do with a gum infection can prevent complications and ensure faster healing.
Do Not Ignore the Symptoms of a Gum Infection
Many people ignore early signs of a gum infection, assuming it will resolve on its own. This is a dangerous assumption. Gum disease begins as gingivitis and can progress to periodontitis if untreated. Common signs include:
- Swollen or red gums
- Bleeding when brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums
- Loose teeth
Ignoring these symptoms allows the infection to spread deeper into the gums and jawbone. Always consult a dentist at the first sign of trouble.
Do Not Self-Diagnose or Self-Treat
Using home remedies or over-the-counter products without professional guidance can worsen gum infections. People often try saltwater rinses, hydrogen peroxide, or essential oils. While these may relieve symptoms temporarily, they do not treat the underlying infection.
Avoid applying substances not approved for oral use. For instance, undiluted hydrogen peroxide or alcohol can irritate the gums further. Professional dental care is the only way to properly diagnose and treat gum disease.
Do Not Postpone Visiting a Dentist
Time is critical when dealing with any oral infection. Delaying a dental visit allows the bacteria to advance, causing more tissue and bone damage. Gum infections do not go away on their own. Instead, they can develop into:
- Chronic periodontitis
- Dental abscesses
- Tooth loss
Early intervention by a dentist can halt the progression of gum disease and help restore oral health.
Do Not Use Tobacco Products
Smoking and using smokeless tobacco worsen gum disease. Tobacco limits blood flow to the gums, which reduces the body’s ability to fight infection. It also masks gum bleeding, hiding one of the main signs of infection.
People who smoke are significantly more likely to develop advanced gum disease. Quitting tobacco is one of the most effective ways to support healing and prevent further dental issues.
Do Not Neglect Oral Hygiene
When gums are sore and bleeding, people often stop brushing or flossing. This is a mistake. Gentle but thorough oral hygiene is critical to controlling bacteria. Avoiding brushing leads to more plaque buildup and worsens the gum infection.
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and non-abrasive toothpaste. Floss gently and consider using antimicrobial mouthwash recommended by your dentist. Maintain regular cleaning to support recovery from gum disease.
Do Not Share Toothbrushes or Oral Care Tools
Gum infections are caused by bacteria, which can spread through saliva. Sharing toothbrushes or oral appliances can transmit harmful microbes to others or even reinfect yourself. Each person should use their own oral hygiene tools to prevent cross-contamination.
Do Not Use Harsh Mouthwashes Without Advice
Some mouthwashes contain alcohol or harsh ingredients that can dry out the mouth or irritate the gums. This can slow healing and cause discomfort. Always use mouthwash as directed by a dental professional, especially when treating an active gum infection.
Do Not Skip Prescribed Medications
If your dentist prescribes antibiotics or antimicrobial rinses, it is essential to follow the full course. Stopping early can lead to drug resistance or a resurgence of the infection. Complete the entire treatment, even if symptoms improve.
Do Not Rely on Painkillers Alone
Over-the-counter pain relievers can reduce discomfort, but they do not treat the infection. Taking ibuprofen or acetaminophen may mask symptoms and delay proper treatment. Painkillers should be used as a temporary aid, not a substitute for dental care.
Do Not Consume Sugary or Acidic Foods
Sugar feeds bacteria in the mouth, worsening gum infections. Acidic foods can also irritate inflamed tissues. During a gum infection, avoid:
- Soft drinks
- Sticky candies
- Citrus fruits
- Processed snacks
Instead, choose a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support healing. Drink plenty of water and avoid snacking between meals to reduce bacterial growth.
Do Not Use Hard-Bristled Toothbrushes
Hard bristles can damage sensitive gums and enamel. This can worsen gum recession and irritation during an infection. Always choose a soft-bristled toothbrush, and brush gently twice a day.
Do Not Underestimate the Severity of Gum Disease
Gum disease is linked to other systemic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. A gum infection is not just a local issue—it affects overall health. Proper treatment and prevention are essential to maintaining both oral and general health.
Do Not Stop Dental Appointments After Initial Healing
Even after your gum infection subsides, continue regular dental visits. Gum disease can return if maintenance is neglected. Your dentist may recommend periodontal maintenance cleanings to monitor and manage gum health over time.
Do Not Use Teeth Whitening Products During Infection
Whitening strips and gels contain peroxides that may irritate infected gums. These products are not meant for use during active gum infections. Wait until your dentist confirms healing before using cosmetic treatments.
Do Not Apply Aspirin Directly on the Gums
This old home remedy is dangerous. Aspirin is acidic and can cause chemical burns when placed directly on soft tissue. If you have gum pain, take pain relievers orally and consult a dentist for safe treatment.
Do Not Skip Flossing
Many avoid flossing when gums are sensitive, but it is essential to remove debris and plaque between teeth. Use waxed floss or interdental brushes for gentler cleaning. Flossing helps prevent further bacterial buildup that could aggravate gum infections.
Do Not Clench or Grind Your Teeth
Bruxism (teeth grinding) increases pressure on the gums and surrounding bone. This can exacerbate gum recession and delay healing. If you grind your teeth, ask your dentist about night guards or other protective options.
Do Not Let Stress Go Unchecked
Stress weakens the immune system and can trigger behaviors like teeth grinding or neglecting oral hygiene. Practice stress management techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or physical activity to support overall wellness and faster healing.
Conclusion
Understanding what not to do with a gum infection is just as important as knowing what to do. Avoiding harmful behaviors and seeking professional care can make the difference between recovery and chronic gum disease.
Gum infections require serious attention. If you notice signs of gum disease, consult your dentist immediately. With the right care and by avoiding common mistakes, you can preserve your oral health and prevent long-term damage.