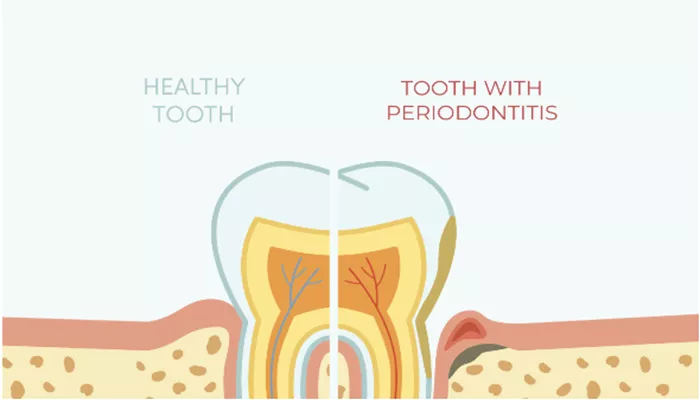
Periodontitis is a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue and, without proper treatment, can destroy the bone supporting your teeth. It often starts as gum disease, also called gingivitis, and if left untreated, progresses into periodontitis. The spread of periodontitis leads to tooth loss and can affect your overall health.
Stopping periodontitis from spreading requires early detection, consistent dental care, and sometimes professional intervention. In this article, we explore detailed ways to control and prevent the progression of this common but dangerous condition.
What Causes Periodontitis to Spread?
Poor Oral Hygiene
Failing to brush and floss regularly allows plaque to build up on teeth and gums. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria, which irritates the gums and causes inflammation. Over time, this inflammation can lead to gum hyperplasia (gum overgrowth) and destroy tissue, letting periodontitis take hold.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking weakens the immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off gum infections. Smokers have a higher risk of periodontitis spreading and responding poorly to treatment.
Systemic Health Issues
Conditions like diabetes, hormonal changes (such as pregnancy or menopause), and certain medications can increase the risk of gum disease and its spread.
Early Signs to Watch For
Detecting periodontitis early can help stop its spread. Symptoms include:
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums or longer-looking teeth
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pus between teeth and gums
If you notice these signs, seek dental advice immediately.
Daily Habits to Prevent Periodontitis Spread
Maintain Proper Oral Hygiene
Brushing your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste removes plaque and bacteria. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and replace it every three months. Flossing daily is equally important to clean between teeth where brushes can’t reach.
Use Antimicrobial Mouthwash
Rinsing with an antimicrobial mouthwash helps reduce bacteria in your mouth and supports gum health. It is especially helpful if you have gum hyperplasia or early gum disease.
Manage Diet and Nutrition
Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins C and D, calcium, and antioxidants strengthens your immune system and promotes gum healing. Avoid excessive sugary foods and drinks that encourage plaque formation.
Quit Smoking
Stopping tobacco use greatly improves your gums’ ability to heal and fight infection. It also increases the success rate of any periodontal treatment.
Professional Treatments to Control Periodontitis
Regular Dental Checkups and Cleanings
Visiting your dentist every six months allows early detection of gum disease. Professional cleanings remove hardened plaque (calculus) that cannot be removed by brushing alone, stopping bacteria from damaging your gums and bone.
Scaling and Root Planing
This deep cleaning procedure cleans bacteria and tartar below the gum line. It smooths the root surfaces, helping gums reattach to teeth and halting further spread of periodontitis.
Antibiotic Therapy
Sometimes dentists prescribe topical or oral antibiotics to reduce bacterial infection. These may be used alongside scaling and root planing for better results.
Surgical Options
In advanced cases, surgery may be necessary. Procedures include flap surgery to clean deep pockets and bone grafts to restore lost bone. Cosmetic dentistry may also be involved to restore gum contours affected by disease or gum hyperplasia.
Addressing Gum Hyperplasia and Its Role in Periodontitis
Gum hyperplasia is an overgrowth of gum tissue, which can worsen periodontitis by creating pockets that trap bacteria. It may result from medications, hormonal changes, or chronic inflammation. Treating gum hyperplasia involves professional cleaning, adjusting medication if possible, and sometimes surgical removal of excess tissue.
How Cosmetic Dentistry Can Help
Cosmetic dentistry is not only for improving aesthetics but can also support gum health. Procedures such as gum contouring and laser therapy can remove diseased gum tissue, improve gum shape, and reduce bacteria-harboring pockets. These treatments complement standard periodontal care and enhance overall oral health.
Importance of Patient Education and Consistency
Patient understanding and commitment are critical to stopping periodontitis. Consistent daily care, awareness of symptoms, and regular dental visits are the foundation of effective disease control. Educate yourself about gum disease and follow your dentist’s recommendations carefully.
Conclusion
Periodontitis is a serious dental condition that can lead to tooth loss and affect overall health if not properly managed.
However, its spread can be effectively stopped through a combination of good daily oral hygiene, lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, and timely professional dental care. Understanding the role of gum disease, gum hyperplasia, and how cosmetic dentistry can aid in treatment helps provide a comprehensive approach to managing periodontitis. Consistency, early detection, and working closely with your dental professional are key to maintaining healthy gums and preventing the progression of this condition. Taking these steps will protect your smile and improve your long-term oral health.